Understanding the Basics of Ionic and Covalent Bonds: A Comprehensive Guide
As a chemistry enthusiast, I am fascinated by the world of chemical bonding. Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms combine to form molecules, and it is the foundation of all matter. In this comprehensive guide, I will walk you through the basics of ionic and covalent bonding. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of the properties of ionic and covalent compounds, the differences between the two, and their importance in everyday life.
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms combine to form molecules. This process occurs when two or more atoms share or transfer electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration. The type of bond that forms between atoms depends on the electronegativity difference between them.
There are three types of chemical bonds:
1-ionic
2-covalent
3- metallic.
In this article, we will focus on ionic and covalent bonding. Ionic bonding occurs between a metal and a nonmetal, while covalent bonding occurs between two nonmetals.
Ionic Bonding
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions. They are also brittle and conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted. Some common examples of ionic compounds include table salt (NaCl), calcium chloride (CaCl2), and magnesium oxide (MgO).
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have several unique properties. They are typically hard and brittle solids that form crystal structures. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between the ions. They are also good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted. Ionic compounds are not soluble in nonpolar solvents such as oil.
Examples of Ionic Compounds
Table salt (NaCl) is one of the most well-known examples of an ionic compound. It is formed by the ionic bonding of sodium and chlorine atoms. Another example is calcium chloride (CaCl2), which is used to melt ice on roads and sidewalks. Magnesium oxide (MgO) is another common ionic compound used in refractory materials.
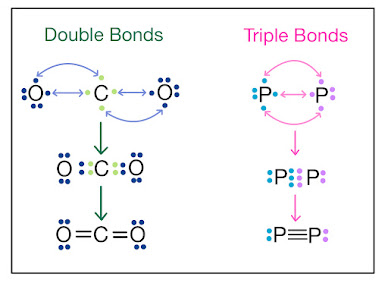
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Unlike ionic bonding, covalent bonding occurs between two nonmetals. Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points and are typically gases or liquids at room temperature.
Properties of Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds have several unique properties. They are typically gases or liquids at room temperature, and they have low melting and boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces. Covalent compounds are not good conductors of electricity, as they do not contain charged particles. They are soluble in nonpolar solvents such as oil.
Examples of Covalent Compounds
It is formed by the covalent bonding of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Another example is methane (CH4), which is the main component of natural gas. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is another common covalent compound that is produced by burning fossil fuels.Water (H2O) is one of the most well-known examples of a covalent compound. It is formed by the covalent bonding of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Another example is methane (CH4), which is the main component of natural gas. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is another common covalent compound that is produced by burning fossil fuels.
Differences between Ionic and Covalent Bonding
The main difference between ionic and covalent bonding is the way in which electrons are shared or transferred between atoms. In ionic bonding, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between two atoms, resulting in the formation of a molecule.
Another difference is the properties of the resulting compounds. Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points, while covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points. Ionic compounds are typically hard and brittle solids, while covalent compounds are typically gases or liquids at room temperature.
Importance of Chemical Bonding in Everyday Life
Chemical bonding is an essential concept in chemistry that has many practical applications in everyday life. For example, the bonding of atoms in water (H2O) is what allows it to exist as a liquid at room temperature. The bonding of atoms in gasoline is what allows it to combust and power our vehicles. Understanding chemical bonding can also help us predict the properties of new materials and develop new technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chemical bonding is the process by which atoms combine to form molecules. Ionic and covalent bonding are two important types of chemical bonding that have unique properties and applications. By understanding the basics of ionic and covalent bonding, we can better understand the world around us and develop new technologies to improve our lives.
Remember, the study of chemistry does not have to be intimidating. With a solid understanding of the basics, anyone can appreciate the beauty of chemical bonding.

.png)







.png)



0 Comments